Attribute Tray
The attribute tray is the primary control for your chart data.
By default, there is one tile for each attribute in your data model in your attribute tray. You can scroll left and right to reveal all of the attributes. The attribute tray immediately allows you to see the measure values for your data as well as filter and breakout data. There are a few actions which every attribute tile allows you to do:
- Breakout an attribute as a series.
- Filter for specific attribute values.
- See measure values for each item immediately.
Hiding and unhiding attribute tiles
You can choose which attributes are visible in the attribute tray. There are two different ways to do this:
- From the data tray, select "show/hide from attribute tray" in the attribute's three-dot menu
- Click the title of a tile or the three-dot icon next to the title and click the eye to hide the tile.
Filtering from the attribute tray
Filters created in the attribute tray are applied across the entire page - filtering every other attribute, the numeric total, and the chart for the values selected in the attribute tile.
The default state for an attribute tile is this filtering mode. Checkboxes next to each attribute value indicate whether the item is included (shown in the exploration) or excluded (filtered out).
- Hover over an attribute value.
- To exclude the value, click it.
- To include just that value, click the icon at the base of the value's measure bar.
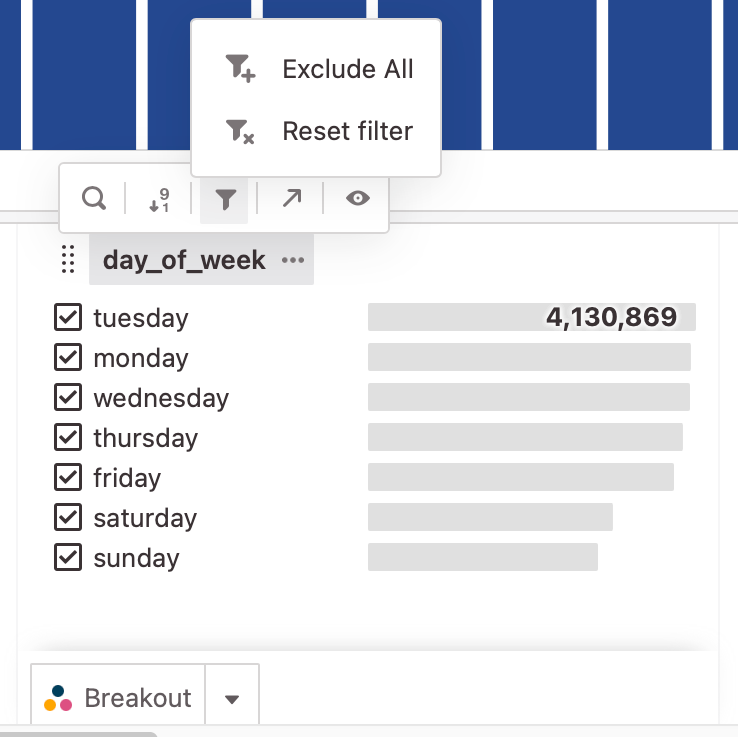
Include vs. exclude filter
- Exclude Items: By default, all items are included. Click an attribute item to uncheck the box and exclude it.
- Include Items: If instead, you want to only include a specific set, click the tile's title, the filter icon, then
Exclude All. All the checkboxes will be emptied and you can select specific items to include.
Exploring further from the attribute tray
You can easily explore and filter other data in your project by selecting this option in the attribute tray:
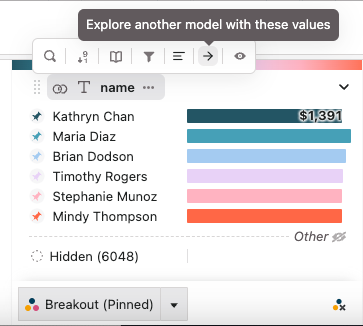
If there's already a filter on the selected attribute, that filter will be preserved. Otherwise, a filter using the first 1000 values from the values shown in the attribute tray will be created.
You can then choose any attribute with the same type from any model in your project. This will take you to an exploration of the selected model with the corresponding filter applied.
Attribute breakout
Adding an attribute as a breakout allows you to layer the attribute onto the current chart. The attribute becomes a grouping of the chart. This is a good way to see changes in the distribution of the attribute over time (or over another numeric interval).
To add an attribute as a breakout:
- Hover over any attribute panel.
- Select the breakout button on the bottom of the panel Breakout.
- To add and remove broken out items, just click on a row.
Breakouts sets are pinned. They do not update when filters or the underlying data changes. If the data has changed significantly, it can be helpful to remove and recreate the breakout.
Sorting attributes
By default, string attributes are sorted by a measure in descending order. To change the order, click the attribute tile's title, then click the sorting icon to see sorting options.
Breakouts can be reordered manually by dragging the attribute items.
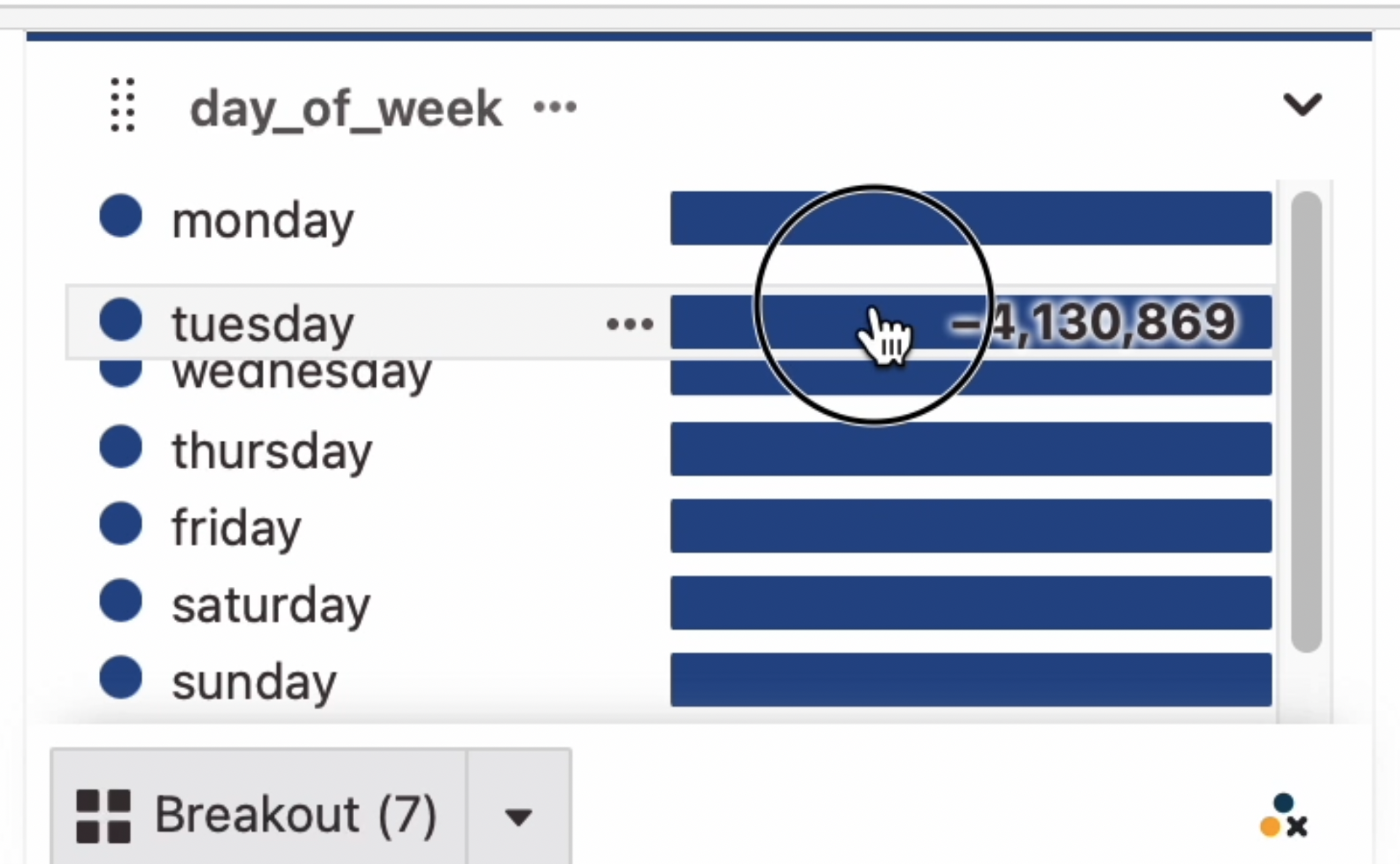
Some notes on sorting attributes:
- If there are a lot of unique items in your list, only the first subset of items are retrieved from the database. Changing the sort order may trigger an additional database query to retrieve the new top of the list.
- Even if there are a lot of items in your list, you can keep scrolling and Glean will automatically pull additional items into the attribute pane as you keep scrolling.
NULLvalues are sorted at the end of a list in descending order (and the top of a list in ascending order).- Behavior of numeric fields is different than strings, see below.
Numeric attributes
Numeric attributes have a few distinct features and differences from the default behaviors of string attributes.
Numeric binning
Attributes are grouped into numeric buckets if binning is turned on for the attribute. The beginning of the range is inclusive and the end value of the range is exclusive. For example, a bucket that is 20 - 25 represents all items that are equal to or greater than twenty and less than twenty-five. You can filter binned numeric data just like you would filter any other attributes-- values in buckets are filtered (or excluded) as you would expect.
The bin size is adjustable via the attribute tile title menu.
Sorting
Unlike string attributes, numeric attributes are by default sorted by their numeric values. This lets you easily see the numeric distribution of the attribute.
Range filters
It is possible to apply a numeric range filter to a numeric attribute by dragging a chart - see the filtering section for additional details.
If a range filter is applied, you can see which values are affected in the attribute panel, but it is not possible to change the range filter from the attribute panel. This is because a range is incompatible with the idea of selecting specific range items.
Array attributes
Array attributes are a powerful feature that allow you to filter and group on elements within array type fields, such as tags. This usually provides greater flexibility and insight than operating with the entire array.
Filtering and breaking out with arrays
Filters and breakouts are applied to individual items within the arrays in your dataset. For example, if your customer contact activity dataset contains arrays representing campaigns, you can use filters to visualize contact activity for a specific campaign only. By breaking out the data, you can examine the distribution of activity across campaigns. Be aware that when using array attributes, Glean unnests the data, which may impact measures, depending on your specific dataset.
For more detailed information about filtering and breakouts, please refer to Filter and Breakout pages.
String attributes
String attributes are alphanumeric attributes and can have very high cardinality (say, millions of unique items). String attributes are searchable to make finding specific attributes easy.
To search for a specific item in a string attribute, click the search icon in the attribute tile title menu.
While searching through a string field is supported, Glean is not optimized for full-text document search. This means that searching through human written comments and long documents is probably not a good idea (mostly it will be slow and potentially costly depending on how those documents are stored in your database).